Nothing slows down warehouse operations like an unexpected error code 853 on your go-to Crown pallet jack.
If you’ve ever seen the 853 code on the Crown Pallet Jack while shuttling pallets to and fro, take a deep breath.
Our forklift expert M.H Nizami has the inside scoop on what this code means and how to fix it.
What does the Error Code 853 mean on a Crown Pallet Jack?
Error code 853 on a Crown pallet jack indicates a throttle mismatch. This means the control system isn’t receiving consistent signals between the throttle position and the actual motor movement.
For example, you may try to accelerate forward but the jack sputters or even moves in reverse. Or the throttle seems “sticky” and is slow to respond as you speed up and slow down. Basically, the jack is confused about what you’re telling it to do with the throttle.

When error 853 pops up on the Crown Pallet Jack, you’ll likely experience jerky, inconsistent, or unexpected movement in the forward and reverse directions. The jack may hesitate before responding to throttle input, or it may take off faster than expected. This unpredictable behavior makes the pallet jack difficult to control and can potentially cause accidents.
The good news?
Some basic troubleshooting and maintenance can often fix error 853 on a Crown pallet jack.
Typical solutions include inspecting and cleaning the throttle potentiometer and associated wiring, checking for loose connections, replacing damaged wires, or replacing the potentiometer if faulty.
Our expert will walk you through these steps to get your Crown jack back up and running smoothly. Keep reading for the full troubleshooting details!
Troubleshooting Error Code 853 on Crown Pallet Jack
There are various troubleshooting methods, depending on the underlying issue causing the error 853 on Crown pallet jacks. Some fixes like repairing short circuits in cable connections are quick, while replacing faulty potentiometers requires more technical work. The complexity of repairs for code 853 ranges from fast fixes to more intensive part swaps, so diagnosing the specific problem is key before beginning any troubleshooting.
➜ Replace Potentiometer or Throttle Card
- Remove the switch cap and disconnect the connectors.
- Replace the potentiometer or throttle card inside the grip.
- Reconnect and reassemble the switch cap.
➜ Replace Control Circuit Fuse (FU3)
- Check the FU3 fuse for damage.
- Test continuity with a multimeter.
- Replace with a new fuse if blown, addressing any underlying issues.
➜ Check Wiring for Opens or Shorts
- Inspect wiring from positive signal to CA205-3 and from B-NEG to CA205-2.
- Use a multimeter to test for continuity and shorts.
- Repair or replace damaged wires.
➜ Confirm Values in Tiller Throttle Menu
- Use the handset controller to access the Monitor menu.
- Navigate to the Tiller Throttle menu and check the Raw Tiller Throttle value.
- Replace the faulty throttle potentiometer if the value on Neutral is not 0.
➜ Check Harnesses and Connections
- Inspect wiring harnesses for damage, particularly at knuckle/pivot points.
- Apply DeoxIT Gold to connectors and recalibrate.
- Replace potentiometers if necessary, especially if stops are worn.
How To Fix Error Code 853 on Crown Pallet Jacks?
Error code 853 on the Crown pallet jack can be frustrating to deal with. Here we have shared the 5 tried-and-tested fixes to try for this fault code.
Fix #1: Replace The Potentiometer or Throttle Card
Error Code 853 on Crown pallet jacks typically results from malfunctioning components within the electronic handle. Specifically, the potentiometer and throttle control card are most likely to blame.
The potentiometer is a sensor that detects the angle of the twist grip and converts it into an electrical signal. This tells the motor how fast to drive the wheels. The throttle control card takes the potentiometer’s signal and regulates the motor speed.
If either component fails, you’ll get error 853 and probably issues with going forward or backward. The potentiometer might not sense the twist grip properly, so the throttle card doesn’t know how fast you want to go. Or the throttle card could be malfunctioning and unable to control the motor, even with a good signal.
These electronic parts are critical for smooth, variable speed control on modern Crown pallet jacks. Older jacks had simple switches, but the twist grip allows precise speed regulation. Losing this makes the jack frustrating to operate.
To fix Error Code 853 on a Crown Pallet Jack, you’ll need to remove the handle’s switch cap and unplug the connectors. Then open up the grip to access the potentiometer and throttle card. Once located, replace either or both components with new parts to resolve the error and restore full functionality to the pallet jack.
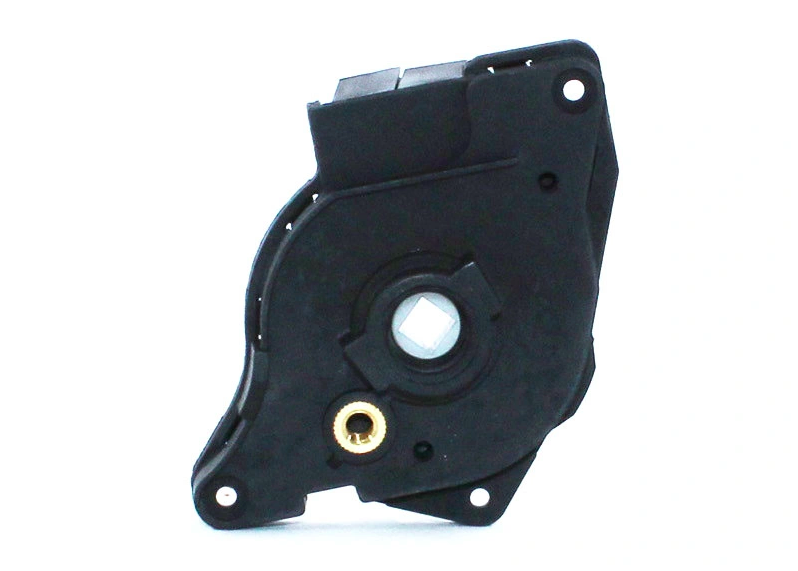

👉 Replacing the Potentiometer:
Here’s a step-by-step guide to fix Crown Pallet Jack error code 853 by replacing the faulty potentiometer or throttle card:
1). Remove the switch cap – Start by unscrewing the bolts that attach the handle’s switch cap assembly to the pallet jack. This will allow you to detach the switch cap from the pallet jack handle so you can access the internal components.
2). Disconnect the electrical connectors – Once the switch cap is off, you’ll see cables and connectors that attach it to the internal electronics. Carefully remove these connectors so you can fully detach the switch cap assembly.
3). Take out the old potentiometer – Inside the switch cap you’ll find the potentiometer, which is the component that needs to be replaced. Remove the screws that hold the potentiometer in place so you can take it out.

4). Install the new potentiometer – With the old potentiometer removed, put the new one in the same spot and secure it with screws. Make sure it is centered properly within the switch cap assembly.
5). Reconnect the electrical components – It’s tricky, but you’ll need to reconnect the cables and connectors to the new potentiometer in the same way they were attached originally. Take your time and be methodical here.
6). Reassemble the switch cap – With all the internal components back in place, you can now reattach the switch cap assembly to the pallet jack handle using the original bolts. Tighten everything back up and you should be good to go.
👉 Replacing the Throttle Card:
If simply replacing the potentiometer doesn’t resolve the 853 error code on your Crown pallet jack, then you need to replace the throttle card.

1). To do this, you’ll need to remove and open up the switch cap assembly on the handle (as explained above).
2). Inside, you’ll find a throttle card located right next to the potentiometer. The throttle card is a small, rectangular-shaped circuit board that controls the throttle input signal from the potentiometer. Over time, the solder joints and components on the card can fail, causing erratic throttle signals.
3). Carefully remove the old throttle card by unplugging the connector and unscrewing any mounting screws.
4). Install a new replacement throttle card, taking care to firmly seat the connector and secure the mounting screws.
5). Once the new throttle card is installed, reassemble the switch cap. With any luck, this should resolve that error code for good. Double-check that the throttle and speed control are working properly before putting your Crown pallet jack back into service.

Fix #2: Replace The Control Circuit Fuse (FU3)
An issue with the control circuit fuse can also cause Error Code 853 on the Crown Pallet Jack.
So make sure to check the condition of the control circuit fuse, also known as the FU3 fuse. This fuse provides power specifically to the pallet jack’s handle and control circuitry.
The FU3 fuse is typically located on the control panel or near the battery on the Crown Pallet Jack. It protects the control circuit from power surges and shorts. If the FU3 fuse is blown, it will cut power to the handle and prevent the pallet jack from operating properly, which can cause error code 853.
Here’s how to troubleshoot it:
1). Visually inspect the FU3 fuse for any signs of damage or a broken filament.
2). Use a multimeter to check for continuity through the fuse.
3). If the FU3 fuse is blown, replace it with an identical new fuse with the proper amperage rating. A blown fuse indicates there may be an underlying short or power issue in the control circuit that will need to be diagnosed and repaired.
4). Replacing the FU3 fuse may allow the pallet jack to operate normally again.
5). But if the error code returns, further electrical testing and troubleshooting will be required. Be sure to fully diagnose and repair any control circuit issues to prevent repeated fuse failure.
Fix #3: Check The Wiring For Any Opens or Shorts
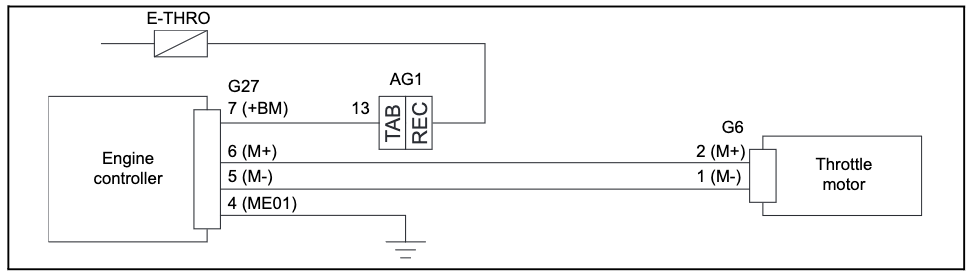
When resolving error code 853 on a Crown pallet jack, you’ll need to check the wiring from the positive signal to CA205-3 and from B-NEG to CA205-2 for any openings or shorts.
CA205-3 and CA205-2 refer to specific pins on the motor controller circuit board that help regulate power to the electric drive motor. The positive signal wire provides power to CA205-3 while the B-NEG wire connects the motor to the ground via CA205-2.
If either of these wires is open (disconnected) or shorted (touching together or touching the ground), it can trigger the 853 error code and prevent the pallet jack’s motor from operating properly.
To check for open or shorted wires, first visually inspect the length of the wires for any obvious damage, cuts, or abrasions in the insulation that could cause a short. Use a multimeter set to continuity mode to test each wire end-to-end for continuity. If you find a break in continuity, that indicates an open wire. You can also use the multimeter to check for shorts between the wires or from each wire to a ground point.
If you confirm an open or short in either the positive signal or B-NEG wiring, you will need to repair or replace the damaged wire to restore proper operation and clear the 853 error code.
Fix #4: Confirm The Values In The Tiller Throttle Menu
Error code 853 can sometimes pop up due to changed value settings in the pallet jack’s computer system. To check if this is the culprit, you’ll need a handset controller for the pallet jack. Crown makes handset controllers that let you access the pallet jack’s computer menus and monitor values.
1). Using the handset, scroll down to the Monitor menu.
2). From there, go to the Tiller Throttle menu, and select Raw Tiller Throttle.
3). Check the value that appears. With the throttle in neutral, the value should be 0. As you move the throttle, the value should change accordingly.
If the values don’t seem right as you operate the throttle, then the likely cause is a faulty POT or potentiometer. The POT is what tells the computer the throttle position. When it goes bad, it can send incorrect values to the computer, resulting in error 853. Replacing the POT, also called the throttle potentiometer, will restore normal operation.
Fix #5: Check The Harnesses and Connections
Harness issues are very common on the old Crown pallet jack models. The wiring harnesses on these older jacks are prone to failure, causing error code 853.
Make sure to check down by the knuckle/pivot point for any wires that may have rubbed through. Also, spray some DeoxIT Gold on all the connectors on the circuit boards. DeoxIT is a contact cleaner, lubricant, and anti-oxidizing solution that can help improve electrical connections. After doing that, recalibrate and see if the code clears up.
If that doesn’t fix it, the potentiometers (POTs) are likely bad. The new replacement POTs come in a kit with new stops for the twist grip. The old stops can wear out which lets the POT rotate beyond its normal range, causing damage. You may need to replace the POT again if the stops are worn.
Most harness issues were fixed in later Crown models. But it helps to know exactly when the 853 code pops up – like only when turning one way or the other. On the older jacks, harnesses often rubbed through under the handle assembly, where they contact the frame. Also, check the harness at the handle stem pivot point. These failure points aren’t always obvious. Intermittent fuse blowing is also a sign of harness failure.
The key is to methodically check the harnesses and connections. DeoxIT and calibration may do the trick. If not, replacing the POT and stops is the next step. Later Crowns improved the harnesses so 853 is less common. But on those temperamental older models, harness, and POT issues are where I’d start troubleshooting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, resolving error code 853 on a Crown pallet jack demands a methodical approach that addresses a range of potential causes, from faulty components to wiring issues and beyond. By conducting thorough inspections and implementing the appropriate fixes, operators can restore optimal functionality to their pallet jacks and ensure smooth operations in their material handling tasks.
Thank you for reading! If you encounter any further issues or have additional questions, please feel free to leave your queries in the comment section below. Our pallet jack expert will be on hand to provide assistance and guidance.