E06-1 and E06-2 on a Toyota Forklift are simply indicators that it’s time for a throttle check. Follow our expert advice for a hassle-free troubleshooting experience, and you’ll have your forklift performing at its best in no time.
Error Code E06-1 and E06-2 on Toyota Forklift: The 3 Main Causes
The best running forklift is thanks to knowing your codes. Remember that E06-1 or E06-2 on the Toyota’s dash is not to be ignored as they are your lift truck’s way of saying something urgent by waving a red flag. Let’s look at what these codes mean and which parts they relate to, so your forklift stays in tip-top condition.
1). Throttle Motor Issue:
The throttle motor in a forklift controls the airflow to the engine, which manages the engine’s power and speed. If there’s an issue with the throttle motor, your Toyota Forklift might show error codes E06-1 and E06-2. This problem can make the engine act up, reduce efficiency, or even totally lose power. That makes it hard to operate the forklift safely and effectively.
2). Wiring Harness Issue:
In forklifts, a wiring harness is the network of wires and connectors that send electrical signals and power through the vehicle. If there’s an issue with the harness, like damaged wires or loose connections, it can mess up communication between different forklift parts. This could set off the E06-1 and E06-2 error codes and could cause the electrical systems to partially or completely fail. That leads to operation problems and potential safety issues.
3). Engine Controller Issue:
The engine controller is basically the forklift’s computer. It manages different engine functions to keep everything running smoothly. An issue with the engine controller could make error codes E06-1 and E06-2 show up. This problem could lead to improper engine management, impacting performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. In bad cases, it could stop the forklift from starting or make it stall while operating.
Resetting Guide
To resolve the error codes E06-1 or E06-2 on a Toyota Forklift, resetting the fault codes can often remedy the issue. However, if the errors continue to appear, it may indicate a malfunctioning throttle or wiring harness connectivity problem that requires troubleshooting.
Here’s how to reset an E06 error on a Toyota Forklift:
- The first step is to disconnect the negative battery terminal for at least 10 seconds. This resets the forklift’s computer system and clears any stored error codes.
- Next, disconnect the water inlet to parts G6 and AG1. Inspect these connections – they bring water into the system for cooling, so any blockages or leaks here can cause overheating issues that trigger an E06 code.
- Reconnect any loose connections. Make sure there’s no corrosion or damage.
- Reconnect the water inlet tubes and battery negative terminal.
- Then, turn the ignition key to the “ON” position to start the engine and check if any error codes are displayed.
- If no errors appear, the issue was likely a loose or corroded connector in the wiring harness. Connector issues can disrupt signals to the forklift’s computer and throttle, causing error codes. Tightening or cleaning the connectors should resolve the problem and prevent the error from returning.
- But if the E06 error remains, there is likely an internal issue with the throttle motor or wiring harness. Further troubleshooting of the throttle and harness circuits will be needed to pinpoint the root cause.
The key points are to first reset the error code, and then inspect the water inlet connections. If the error returns, it indicates a deeper issue that requires advanced troubleshooting of the throttle and wiring.
E06-1 and E06-2 Error Code Troubleshooting Guide
As shared above, error code E06-1 or E06-2 in most cases boils down to one of three components – the throttle motor, wiring harness, or engine control unit. The tricky part is figuring out which one. Instead of a shotgun approach, let’s walk through the step-by-step troubleshooting guide.
I’ll explain the telltale signs of each potential culprit, tests to perform, and how to zero in on the root cause. By working together to isolate the source of the problem, you can get your forklift operating optimally once again.
1). Throttle Motor Resistance Inspection
First up, you need to carry out a throttle motor inspection. This involves testing the motor itself separately from the rest of the system.
- To do this, turn the ignition key switch OFF first.
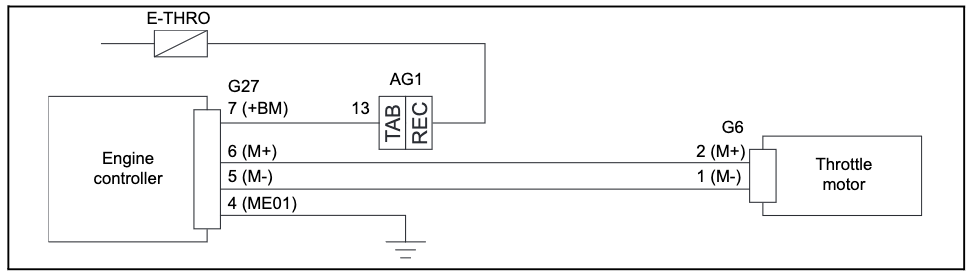
- Then, disconnect connector G6 and connect connector G27 instead. G6 is the main throttle motor connector while G27 allows us to test the motor individually.
- Now we can check the throttle motor resistance.
- Use your multimeter probes to measure between pins G6-2 and G6-1 on the motor side.
- The standard readings we’re looking for are: 0.3 to 100 ohms at 20°C.
- We want the resistance reading to be somewhere between 0.3 and 100 ohms when the motor is at room temperature. If the reading is way outside this range, there’s likely an issue with the motor’s resistance internally. This could be due to worn-out windings or bad connections.
| G6-2 ~ G6-1 | 0.3 ~ 100 Ω (20°C) |
When resistance is the culprit, there are a few ways you can get things back in shape:
- Clean the motor connectors and pins to clear any corrosion or dirt buildup causing high resistance. Use electrical contact cleaner spray.
- Test the motor windings for opens or shorts. If found, the motor will likely need replacement.
- Check wiring between the motor and ECU for damage that could introduce resistance. Repair any cuts, fraying, etc.
The key is zeroing in on any resistance abnormalities and eliminating their cause.
2). Throttle Valve Drive Condition Inspection
If the throttle motor checks out okay, the next step is to take a look at the throttle valve. There are a couple of standard checks to perform to ensure the valve is working right:
1. The throttle valve should operate smoothly when fully opened. This means when you push the throttle down, it should move smoothly without catching or sticking. If it does not operate smoothly, it could indicate a mechanical issue like binding, contamination, or wear and tear.
2. The throttle valve should operate smoothly when fully closed. Similarly, when you let off the throttle and it returns to the closed position, it should move smoothly back to closure. Any sticking, catching, or uneven movement could signify a problem.
3. The throttle should return to opener angle when released. When you let go of the throttle, it should spring back to the idle/opener angle position. If it sticks part-way, doesn’t return at all, or goes past the opener angle, it suggests an issue with the return spring or mechanism.
Overall, the throttle valve needs to move through its full range of motion smoothly and precisely, both when actuated and when returning. Any deviation from the standard values indicates a potential issue needing diagnosis and repair. Binding, sticking, contamination in the mechanism, or spring and linkage wear could all contribute to abnormal operation.
3). Harness Continuity and Short-Circuiting Inspection
Once you’ve ruled out problems with the throttle motor and throttle valve drive on your Toyota forklift, it’s likely an electrical issue triggering the E06-1 and E06-2 error codes. The wiring harness, which relays power and signals through the forklift, may have continuity or short circuit problems.
Here’s how to inspect the harness for continuity and short-circuiting:
1. Turn the ignition key switch to the OFF position.
2. Disconnect connectors G27 and G6.
3. Then, use a multimeter to check for continuity between the following points:
- G27-6 to G6-2: You should find continuity here.
- G27-5 to G6-1: Continuity should also be present here.
4. You should also ensure there is no continuity between these points:
- G27-6 to the Frame
- G27-5 to the Frame
- G27-6 to G27-5
- G27-6 to G27-7
- G27-5 to G27-7
| G27-6 ~ G6-2 | Continuity |
| G27-5 ~ G6-1 | Continuity |
| G27-6 ~ Frame | No Continuity |
| G27-5 ~ Frame | No Continuity |
| G27-6 ~ G27-5 | No Continuity |
| G27-6 ~ G27-7 | No Continuity |
| G27-5 ~ G27-7 | No Continuity |
If any of those readings are out of spec, there’s likely a wiring issue causing the E06-1 code. A break in continuity means there’s an open circuit, while unwanted continuity points to a short circuit. Make sure to thoroughly inspect the harness connectors and wires. Look for chafing, bare wires, corroded terminals, etc. Repair or replace any damaged wiring as needed.
Summary
When you see the E06-1 and E06-2 error codes flashing on your Toyota forklift, it’s a sign that something’s up with the throttle system. These codes mean there could be issues with the throttle motor, wiring, or engine control unit. To fix it, you need to follow some steps. First, reset the error code. Then, check the water inlet connections. After that, test the throttle motor’s resistance and valve. Finally, inspect the wiring harness for any issues. By doing these steps, you can find out what’s wrong and get your forklift back to working well and safely.
