The error code 100-4 tends to pop up on big commercial trucks and industrial vehicles like forklifts. You might see it as SPN 100/FMI 4 on your Cummins’ display. Or error code 100-4 blinking on your Yale or Hyster forklift. Either way, it’s pointing to an issue with oil pressure. Specifically, low oil pressure in the engine.
So if you see that 100-4, it means the oil isn’t flowing strongly enough to properly lubricate all the moving parts under the hood. When the oil pressure drops, the oil can’t do its job keeping the pistons, valves, and bearings happily sliding and turning. The engine strains and struggles, and over time the damage builds up.
The code 100-4 illuminates to warn the driver there’s a problem that needs addressing fast. If left unfixed, the consequences can be dire — busted gaskets, seized pistons, worn out bearings, and sometimes complete engine breakdown. But with prompt troubleshooting, the root cause can be found and resolved before costly repairs are needed.
The good news is this post will provide a complete troubleshooting guide for fault code 100-4. I’ll walk you through how to track down the root cause and get that oil flowing safely again.

Why & When 100-4 Fault Code Shows Up In Your Vehicle?
The 100-4 or SPN 100/FMI 4 error message pops up on the dashboard display when the engine’s electronic control unit (ECU) senses low oil pressure. The ECU is the electronic brain monitoring all aspects of engine operation, so it takes oil pressure very seriously. If the oil pressure drops too low, there will be a lack of oil circulation to keep the engine lubricated. This might cause grinding of the engine parts and excessive wear and tear to them.
When the ECU detects the oil pressure has fallen below the normal range, it will trigger the 100-4 code to appear on your dashboard display to warn you there’s a problem. At this point, the lack of oil flow is not good for your engine and continued driving could cause permanent damage.
There are a few possible causes for low oil pressure that would lead to this code appearing. It could be a faulty oil pressure sensor or wiring, a short in the sensor circuit, or the oil pressure sensor itself going bad.
💡 Error Code 100-4 (SPN 100 / FMI 4) vs Error Code 100-3 (SPN 100 / FMI 3)
Error code 100-4, also referred to as SPN 100 / FMI 4, indicates a situation of low oil pressure in the forklift or the truck’s engine.
On the other hand, error code 100-3, also known as SPN 100 / FMI 4, signifies high oil pressure in the forklift or the truck’s engine.
Both error codes share a common characteristic in that they identify abnormalities in the oil pressure of the vehicle’s engine. However, they differ in terms of the specific issue they highlight. Error code 100-4 targets low oil pressure, while error code 100-3 targets high oil pressure.
The diagnostic and troubleshooting process is consistent for both fault codes. In the case of 100-4, verify that your forklift engine’s oil pressure falls within the standard range. For 100-3, ensure the oil pressure isn’t higher than the standard range.
Possible Causes
There are five possible reasons why the error code 100-4 may show up on your Cummins, Detroit Diesel, or Yale equipment. I’ll explain each of these potential issues in detail below:
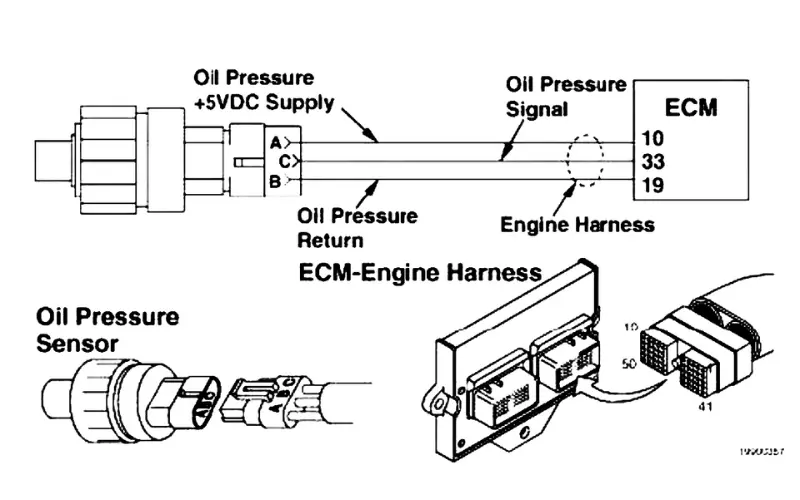
1). Faulty Engine Harness Connecting the Oil Pressure Sensor
The engine harness connecting the oil pressure sensor could be the reason behind error code 100-4. It is possible that the connector has pushed back or expanded pins, bent or broken pins, or corroded pins. These issues can disrupt the connection between the sensor and the engine harness, causing the error code to appear.
2). Moisture in or on the Connector
Another potential cause of error code 100-4 is moisture in or on the connectors connecting to the oil pressure sensor. Moisture can interfere with the electrical signals being transmitted through the connector, leading to an erroneous reading from the oil pressure sensor. This can trigger the error code and indicate a problem with the engine harness.
3). Missing or Damaged Seals
Missing or damaged seals in the oil sensor’s harness can also contribute to error code 100-4. Seals are crucial for maintaining a proper connection and preventing moisture or other contaminants from entering the connector. If these seals are missing or damaged, it can compromise the integrity of the connection and trigger the error code.
4). Low Engine Oil
The ‘100-4’ fault code could also be triggered due to low oil levels in your vehicle’s engine. Oil’s what keeps your engine’s insides running smooth, and without enough of it, you’ll grind those parts to dust in no time.
Now oil levels drop for a couple reasons. Maybe you’ve sprung a leak somewhere, in which case you’ll want to get under there and find it quick before you’re bone dry. But more often it’s just that you’ve gone too long between oil changes, or burned some off driving too hard. Whatever the case, best check your levels pronto.
Checking your oil isn’t a complicated thing. Pop the hood, locate the dipstick – that’s the handle with the yellow top that says ‘oil’ on it. Pull it out, wipe it clean, slide it back in, then pull it out again. Check the markings on the end of the stick, see where the oil line is. If it’s low, time to add a quart or three.
Now, if that dipstick showed your oil was low, here’s what you do. Make sure you’ve got the right oil for your engine – check the manual if you’re unsure. Unscrew the oil fill cap and top it off a quarter quart at a time, rechecking the dipstick as you go. Keep adding small amounts until the level reads full. Replace the fill cap when you’re done.
5). Faulty Oil Pressure Sensor
The oil pressure sensor is usually a little metal cylinder with some wiring attached. It’s mounted somewhere on your engine block, immersed in the oil flow. When the oil is pumping strong and true, that sensor remains content and quiet. But if it detects oil pressure dropping too low, it hollers for help by triggering the SPN 100/FMI 4 code.
To check if your oil pressure sensor has gone faulty, first look for any visible damage to it. See if the wiring is frayed or disconnected, or if the sensor body itself is cracked or broken. You can also get a mechanical oil pressure gauge and compare the sensor’s reading to the gauge’s — if they differ by a fair amount, the sensor probably needs replacement.
Troubleshooting Guide
Troubleshooting error code 100-4 requires a thoughtful, step-by-step approach. We must not rush to complex diagnoses before testing the basics. Methodical troubleshooting reveals the root cause.
➜ Typically we’d start by checking the open circuit. Verify all connectors fit snug and no wires look damaged. Wiggle things around while watching for intermittent power loss. That sort of thing. Just common sense open circuit testing.
➜ Next we inspect the engine oil pressure sensor wiring. Unplug the sensor and check the harness and pins for corrosion or loose/broken connections. Ohm out the wires checking for shorts to ground or power. Replace damaged wires if needed. You get the idea – standard wiring diagnostics.
➜ Finally we test the oil pressure sensor itself. If no wiring faults appeared in the last step, replace the suspect sensor, clear any codes, and retest for proper operation. The new sensor should fix it if the wiring checks out.
Here’s a complete step-by-step troubleshooting guide for error code 100-4 or SPN 100/FMI4:
Step #1 – Inspecting the oil pressure switch and engine harness connector pins.
Turn the key switch OFF and disconnect the engine harness from the oil pressure switch. Inspect the oil pressure switch and the engine harness connector pins for the following:
- Pushed back or expanded pins
- Bent or broken pins
- Corroded pins
- Moisture in or on the connector
- Missing or damaged seals
| Are the pins damaged? | |
| If not, go to the next step. | If yes, repair or replace the oil pressure switch or the engine harness, whichever has damaged pins |
Step #2 – Inspecting the engine harness and ECM connector pins.
Turn the key switch OFF and disconnect the engine harness from the ECM. Inspect the engine harness and the ECM connector pins for the following:
- Pushed back or expanded pins
- Bent or broken pins
- Corroded pins
- Moisture in or on the connector
- Missing or damaged seals
| Are the pins damaged? | |
| If not, go to the next step. | If yes, repair or replace the engine harness or ECM, whichever has damaged pins. |
Step #3 – Inspecting an open circuit.
Turn the key switch OFF and disconnect the engine harness from the oil pressure switch. Disconnect the engine harness from the ECM.
Check for an open circuit. Measure the resistance from pin of the engine harness connector to the oil pressure switch connector.
| Are the ohms within the standard range? | |
| If yes, go to the next step. | If not, replace the engine harness. |
Step #4 – Inspecting a circuit to ground.
Turn the key switch OFF and disconnect the engine harness from the oil pressure switch. Disconnect the engine harness from the ECM.
Check for a short circuit to ground. Measure the resistance from the pin of the engine harness connector to engine block ground.
| Are the ohms within the standard range? | |
| If yes, go to the next step. | If not, replace the engine harness. |
Step #5 – Inspect for a short circuit from pin to pin.
Turn the key switch OFF and disconnect the engine harness from the ECM. Disconnect the engine harness from the oil pressure switch.
Check for a short circuit from pin to pin. Measure the resistance from the pin of the engine harness connector to all other pins in the engine harness connector.
| Are the ohms within the standard range? | |
| If yes, replace the oil pressure sensor. | If not, replace the engine harness. |
🚜 How to Find the Correct Pin to Measure Resistance?
Determining the correct pin to measure resistance in an engine harness can vary depending on the specific vehicle or equipment model. However, there are general steps you can follow to identify the correct pin:
1. Consult the Service Manual: The most reliable method is to refer to the service manual of the specific forklift or truck model you’re working on. The manual typically includes a wiring diagram that indicates the pin numbers and their functions.
2. Trace the Circuit: If you don’t have access to the service manual, you can trace the circuit from the oil pressure switch back to the engine harness connector. This may help you identify which pin corresponds to the oil pressure switch.
3. Use a Multimeter: Set your multimeter to the resistance (ohms) setting and test each pin in the engine harness connector until you find the one that shows continuity with the oil pressure switch connector. This is the pin you would measure for resistance.
Resolving Fault Code 100-4 or SPN 100/FMI 4 in Trucks and Forklifts
Getting fault code 100-4 on your Cummins truck or Yale Forklift?
No worries, we can figure this out. There’s a process to follow with a few key steps that should get us to the bottom of it.
Let me share the diagnosis steps so you know how to resolve this error code.
Fix #1: Do the cables connecting to the oil pressure sensor appear to be in good shape?
As an experienced mechanic, I always start by checking the connectors and wiring harness leading to the oil pressure sensor.
The oil pressure sensor’s wiring harness and connectors play a pivotal role in the accurate transmission of electrical signals and power to and from the oil pressure sensor.
Inside these connectors or switches attached to the oil pressure sensor are little metal pins that carry signals from the oil pressure sensor back to the forklift’s electronic control unit (ECU). The ECU processes these signals to monitor and adjust the forklift’s performance in real-time.
If a pin is bent or broken, it may still make contact but could deliver intermittent signals, leading to fluctuating readings that do not represent the actual oil pressure.
This causes the ECU to register an abnormal oil pressure error due to the lack of data.
So the first step when it comes to troubleshooting fault code 100-4 is to turn the key switch OFF and disconnect the engine harness from the oil pressure switch. And then Inspect the oil pressure switch and the engine harness connector pins for the following:
➜ Bent or Broken Pins: Connector pins on the oil pressure sensor’s harness are responsible for transmitting electrical signals from the sensor to the ECU. Bent or broken pins can disrupt this signal, leading to inaccurate oil pressure readings. This can cause the ECU to misinterpret the oil pressure, potentially resulting in improper engine adjustments or a failure to alert when oil pressure is out of the normal range.
➜ Pushed Back or Expanded Pins: If the pins are pushed back or expanded, they may not make proper contact with the corresponding receptacles in the connector. This can lead to intermittent or weak signals, causing fluctuating oil pressure readings that confuse the ECU and lead to erratic engine behavior.
➜ Corroded Pins: Corrosion on the pins can be caused by exposure to moisture or chemicals, leading to increased electrical resistance. High resistance can weaken the signal from the sensor, causing the ECU to receive incorrect information about the engine’s oil pressure.
Moisture in or on the Connector: Moisture can cause short-circuits or corrosion, both of which can interfere with the electrical signals passing through the connector. This can result in the ECU receiving no signal or a faulty signal, which may trigger an oil pressure error.

Fix #2: Is there trouble with the EOP sensor circuit?
The error code 100-4 on a forklift means there’s trouble with the Engine Oil Pressure (EOP) sensor circuit.
When the oil pressure sensor circuit has an electrical short to ground, it sets off this code.
This circuit relays the oil pressure from the engine to the computer, so the computer knows if there’s enough juice lubricating all those churning parts. Oil pressure is key because without enough of it, the engine can’t lubricate itself properly. Parts grind and overheat.
Now a short to ground means somewhere along that wire path electricity is leaking straight to the body of the forklift rather than following the route to the computer. Could be a fray in the wires, the sensor itself gone kaput, or a loose connection letting the current sneak away.
When the oil pressure sensor circuit is short to ground, the sensor can send the wrong signals to the forklift’s computer. The computer might think there’s too little oil pressure when there’s really enough. Or it may get no signal at all.
If the forklift’s computer gets the wrong oil pressure readings, the engine won’t run right. The computer may think the oil pressure is too low to operate safely. So the engine could run rough or even shut off to avoid damage.
The fix here is to track down the short circuit. Check connections are tight, wires intact, and the sensor itself is in working order. The computer needs good intel to manage the engine properly. Once you get that oil pressure data flowing right again, the computer can relax and let the engine run as it should.
Fix #3: Has the voltage from the engine oil pressure switch dropped below the acceptable threshold?
Fault code 100-4 also means that the voltage from the engine oil pressure sensor has dipped below the acceptable threshold.
In simpler terms, the forklift’s ECU has detected that the voltage signal received from the engine oil pressure sensor is too low, which suggests that the oil pressure within the engine might be insufficient.
But why does this voltage system exist?
Well, it serves as a crucial monitoring mechanism to ensure that the engine oil pressure remains within the acceptable range. By measuring the voltage, the forklift can identify any potential issues with the engine’s oil pressure.
Typically, for most forklift models, the voltage range lies between 4.5 and 5.5 volts.
Talking in the context of the engine oil pressure’s voltage issue, the error code 100-4 could arise due to several reasons:
Firstly, the oil pressure sensor itself might be malfunctioning or have completely failed, resulting in the transmission of an incorrect low voltage signal. Additionally, there could be problems with the wiring connected to the oil pressure sensor, such as a short circuit or disconnection, causing a disruption in the voltage signal.
However, it is also essential to recognize that the engine could genuinely be experiencing low oil pressure. This can stem from various factors, including a low oil level, worn engine components, or even a faulty oil pump.
In some cases, the forklift may even enter a “limp mode,” where its performance is restricted to prevent any further damage. This serves as a protective measure, ensuring that the forklift is not operated under unfavorable conditions, which could lead to severe engine damage.
Therefore, it becomes imperative to address the issue promptly to prevent any further damage.
Fix #4: Are there any missing or damaged seals on the switch or harness?
Error code 100-4 on a forklift can be attributed to the absence or deterioration of seals within the oil pressure switch or the harness. When those seals start leaking or go missing, the oil doesn’t build up the pressure it needs, and the engine doesn’t get the oil it’s hankering for.
Without that oil pressure, your forklift’s engine can overheat right quick. The pistons and valves don’t get the lubrication they need and end up scraping themselves raw. It’s a sorry state of affairs, to be sure. Those seals and the harness are there to make sure the oil flows smooth and steady, keeping your engine running cool and clean.
There are several factors that can contribute to the damage or loss of these seals. For instance, regular wear and tear over time can cause deterioration, especially if the forklift is subject to demanding working conditions or insufficient maintenance. Additionally, accidental impact or mishandling during maintenance procedures can result in the seals becoming damaged or displaced.
The fix is simple. Replace those worn out seals with new ones, make sure they’re seated properly. Then that forklift will run clean as a whistle. Engine will fire right up, oil will flow smooth as silk, and voltage will be steady as the forklift goes!
Fix #5: Could the oil pressure sensor be malfunctioning?
The 100-4 fault code can also come up when there’s an issue with the oil pressure sensor in the engine. In most forklifts, the oil pressure switch sits on the engine block, typically below and to the right of the electronic control module. There are a few ways to check if the oil pressure sensor is working properly or not:
➜ A failing oil pressure sensor can make the engine noisy or the timing chain rattle. You’ll hear a low, metallic rattling from the engine, especially if the timing chain is fed oil and the tensioners lose pressure. The bad sensor isn’t detecting the oil pressure dropping, so the engine sounds off. The most surefire way is to manually check the oil pressure with a gauge. If the gauge shows good oil pressure but the dash light is on, it’s probably a bad sensor.
➜ Sometimes a faulty oil pressure sensor leaks oil too, which you’ll spot around where the sensor sits. Oil can seep past the sensor’s bad seal, dripping onto the engine. A failing sensor may get oil on its body, a sign it’s leaking.
➜ Look for corrosion or damage on the sensor or its plug. Exposure to the elements in the engine bay can corrode the sensor, and physical harm can also cause issues.



⛽ How To Check If The Oil Pressure Sensor Needs Replacement?
To check if your oil pressure switch has gone south, you’ll want to get your hands on an oil pressure testing kit.
Once you have the necessary tools for the job, start by locating the oil pressure switch, usually found on the engine block.
Loosen the switch, being careful not to strip the threads, then install the oil pressure testing gauge in its place.
Start up your forklift to circulate the oil, and check the reading on your gauge.
If it’s lower than the specification in your owner’s manual, you likely have a short circuit or a faulty harness. However, if the pressure is normal, you have a bad oil pressure switch and simply need to replace it to get back to work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, resolving the error code 100-4 in your forklift or truck is not always a straightforward fix. And often, it requires a bit of detective work to pinpoint the exact cause. Whether it’s a faulty harness, short-circuited wires, or an issue with the oil pressure sensor itself, each scenario demands a careful approach.
For some, the resolution might be as simple as replacing a worn-out harness that has seen better days. For others, it could involve tracing and repairing short circuits that are causing havoc in the electrical system. And then there are times when the oil pressure sensor is the culprit.
How did you resolve the fault code 100-4? Was it a matter of swapping out the harness, or did you find yourself untangling a web of electrical shorts? Or perhaps it was the oil pressure sensor that needed your attention. Share your experiences and solutions in the comments below.
